Affect vs. Effect: Stop Confusing Them for Good
Incorrect usage of the words ‘affect’ and ‘effect’ is incredibly common! English language learners, non-native English speakers, and even native English speakers find it challenging to correctly choose between ‘affect’ and ‘effect’. Although these two terms have similar spellings and pronunciation, ‘affect’ and ‘effect’ are not interchangeable and, in fact, have distinct meanings and functions in sentences.
In this article, we will explain the meanings of ‘affect’ and ‘effect’, the difference between these two terms, and tell you some easy ways to remember which one to use in any situation. First, let’s take a look at exactly what the words ‘affect’ and ‘effect’ mean.
Affect vs. Effect Meaning
To learn how to use ‘affect’ and ‘effect’ you must first understand the distinct meanings of these two terms. Although they are spelled and sound similar, they play different roles grammatically and carry distinct meanings.
Affect Meaning
Affect is most commonly used as a verb. In this context, ‘affect’ means to influence or to have an impact on something. For example, “The weather can greatly affect your mood.” Here, the weather has the power to influence or change your mood.
Although ‘affect’ is most commonly used as a verb, it can also be used as a noun within the realm of psychology. In this case, ‘affect’ refers to an emotion or subjectively experienced feeling. For example, “The therapist observed a flat affect in the patient, indicating a lack of emotional expression.” However, this usage is much less common and is only usually found in specific psychological or clinical contexts.
Effect Meaning
‘Effect’ is primarily used as a noun to signify a result or outcome. For instance, in the sentence “The effect of the medication was immediate,” the word ‘effect’ refers to the result of taking the medication.
‘Effect’ can, however, also be used as a verb in some instances, although this is less common. When used as a verb, ‘effect’ means to bring about or cause something to happen. For example, “The government hopes to effect change with its new policy.” In this sentence, the government is aiming to cause change or make it happen.
Affect vs. Effect Example Sentences
Affect Example Sentences
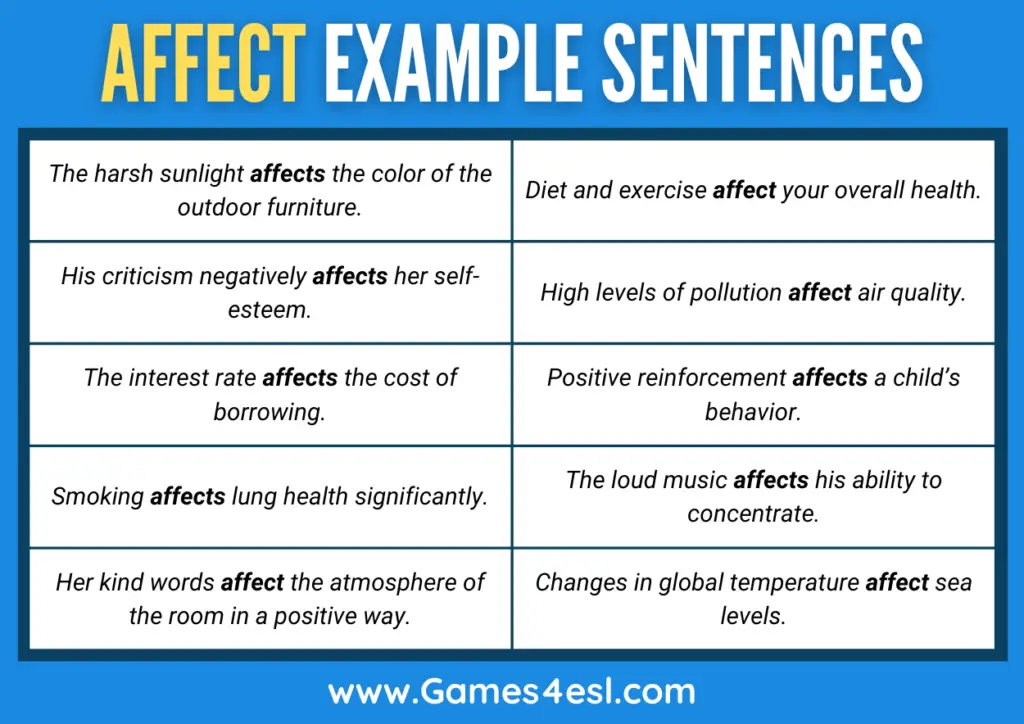
Here are 10 example sentences using ‘affect’ as a verb, which is the most common usage of the word ‘affect’.
| Example Sentence | Explanation |
|---|---|
| The harsh sunlight affects the color of the outdoor furniture. | The harsh sunlight causes a change in the color of the outdoor furniture. |
| His criticism negatively affects her self-esteem. | His criticism negatively impacts her self-esteem. |
| The interest rate affects the cost of borrowing. | The interest rate influences/causes a change in the cost of borrowing. |
| Smoking affects lung health significantly. | Smoking has an adverse or negative impact on lung health. |
| Her kind words affect the atmosphere of the room in a positive way. | Her kind words influence the atmosphere of the room in a positive way. |
| Diet and exercise affect your overall health. | Diet and exercise influence or cause changes in your overall health. |
| High levels of pollution affect air quality. | High levels of pollution have a negative impact on air quality. |
| The loud music affects his ability to concentrate. | The loud music negatively influences his ability to concentrate. |
| Positive reinforcement affects a child’s behavior. | Positive reinforcement influences or causes a change in a child’s behavior. |
| Changes in global temperature affect sea levels. | Changes in global temperature influence or cause a change in sea levels. |
Effect Example Sentences

Here are 10 example sentences using ‘effect’ as a noun, which is the most common usage of the word ‘effect’.
| Example Sentence | Explanation |
|---|---|
| The green effect on the wall gives a calming ambiance. | In this sentence, ‘effect’ is a noun referring to the result or outcome created by the color green on the wall, contributing to a calming ambiance. |
| His words have a strong effect on the audience. | In this sentence, ‘effect’ is a noun referring to the significant impact or influence that his words have on the audience. |
| The medication has the side effect of drowsiness. | In this sentence, ‘effect’ is a noun referring to the additional, usually unintended result of taking the medication, which is causing drowsiness. |
| The butterfly effect explains how small actions can have large consequences. | In this sentence, ‘effect’ is a part of the term ‘butterfly effect’, which refers to the concept that small actions or events can lead to large, sometimes unpredictable, outcomes or consequences. |
| The lighting in the room produces a dramatic effect. | In this sentence, ‘effect’ refers to an impression or mood created by something, in this case, the lighting in the room. |
| The law is in effect as of today. | Here, ‘effect’ means something that has been officially started or implemented, referring to the law in this case. |
| The sound effect enhances the movie experience. | In this context, ‘effect’ refers to a sound artificially created or enhanced for a film, broadcast, or musical recording. |
| The cause-and-effect relationship is fundamental in scientific studies. | Here, ‘effect’ is part of the phrase “cause and effect,” which refers to the principle of causality, where an action or event will produce a certain response. |
| The greenhouse effect contributes to global warming. | ‘Effect’ refers to a scientific phenomenon where gases in the earth’s atmosphere trap heat, contributing to global warming. |
| The special effects in the film are impressive. | In this case, ‘effect’ refers to artificial or digitally created visual elements in a film. |
Affect vs. Effect? Easy Ways To Remember Which To Use

If you still find it difficult to figure out whether to use ‘affect’ or ‘effect’ in any given sentence, then here are some general rules and tips you can use to help:
Verb or Noun?
Most commonly, ‘affect’ is used as a verb, and ‘effect’ is used as a noun. So, look at the sentence you are trying to make and check whether you want the word to function as a verb or noun. If it’s a verb, use ‘affect’; if it’s a noun, use ‘effect.’ Of course, there are exceptions to this rule, but this method of remembering which one to use will work in the vast majority of sentences.
A for Action
Another way to remember whether to use ‘affect’ or ‘effect’ is to remember ‘A for Action.’ If you are describing an action, use ‘affect.’
E for End Result
Just like the above tip, if you remember ‘E for End Result,’ you can know whether to use ‘effect’ or ‘affect.’ Just remember ‘E’ if for ‘Effect’ and ‘E’ is for ‘End.’ So, if your sentence is about an end result of something, use ‘effect.’
RAVEN
This is an acronym that stands for Remember Affect (is a) Verb Effect (is a) Noun. If you can remember this acronym, you should easily remember whether to use ‘affect’ or ‘effect’ in your sentences.
Affect vs. Effect: Common Causes of Confusion
The terms ‘affect’ and ‘effect’ cause a lot of confusion for English language learners, teachers, and English native speakers alike. But why is this so? Here are some of the common causes of this confusion.
Similar Spelling and Pronunciation
One of the main reasons for confusion between ‘affect’ and ‘effect’ is their strikingly similar spelling and pronunciation. With just one letter differing, it’s easy to see how they can be mistaken for each other. Moreover, their pronunciation is nearly identical, adding to the likelihood of error.
The Exceptions To The Rule
As previously mentioned, ‘affect’ and ‘effect’ don’t always stick to their most common roles as a verb and noun, respectively. ‘Affect’ can be used as a noun in psychological contexts, and ‘effect’ can be used as a verb, meaning to cause or bring about something. These less frequent usages often lead to further confusion, as they break the usual rule of ‘affect’ as a verb and ‘effect’ as a noun.
Misconceptions and Common Errors
Over time, misconceptions about these two words have arisen. For instance, some people might mistakenly believe that ‘affect’ is used only in negative contexts, while ‘effect’ is used in positive ones. This is not true, as both words can be used regardless of the sentiment of the situation. Such misconceptions and frequent errors in writing and speech contribute to the ongoing confusion surrounding ‘affect’ and ‘effect.’
Variations Of ‘Affect’ And ‘Effect’
In addition to finding ‘affect’ and ‘effect’ confusing, their variations are also regularly misused. These variations include ‘affected’ vs ‘effected’, ‘affects’ vs ‘effects’, ‘affective’ vs ‘effective’, and ‘affecting’ vs ‘effecting’. Let’s look at each of these one by one.
‘Affected’ vs. ‘Effected’
‘Affected’ is the past tense of ‘affect’ and means ‘influenced’ or ‘changed.’ ‘Effected’ is the past tense of the less commonly used verb form of ‘effect’ and means ‘brought about’ or ’caused.’. Here are some example sentences with ‘affected’ and ‘effected’:
His sleep was affected by the loud noise outside.
The drought affected the farmer’s crops severely.
The new president effected significant policy changes.
The company effected major restructuring after the merger.
‘Affects’ vs. ‘Effects’
‘Affects’ is the third person singular present of ‘affect’ and means ‘influences’ or ‘impacts’. Effects’, in contrast, is the plural of ‘effect’ and refers to results or outcomes. Here are some example sentences with ‘affects’ and ‘effects’:
Exercise positively affects overall health.
His decision affects everyone on the team.
The effects of climate change are evident.
The side effects of the medication include dizziness and nausea.
‘Affective’ vs. ‘Effective’
‘Affective’ is an adjective relating to moods, feelings, and attitudes. ‘Effective’, on the other hand, means successful in producing a desired result. Here are some example sentences with ‘affective’ and ‘effective’:
Music has an affective impact on people.
Affective disorders include conditions like depression and bipolar disorder.
The campaign was effective in raising awareness about mental health.
Physical distancing is an effective measure to prevent diseases.
‘Affecting’ vs. ‘Effecting’
‘Affecting’ is the present participle of ‘affect’, meaning having an impact on. ‘Effecting’, on the other hand, is the present participle of the less common verb form of ‘effect’, meaning bringing about or causing. Here are some example sentences using ‘affecting’ and ‘effecting’:
The lack of rainfall is severely affecting the crops
Climate change is affecting weather patterns worldwide.
The council is effecting changes to the local zoning laws.
The leadership is effecting a new approach to internal communication.
Wrapping Up
Thanks for reading! I hope you now have a better understanding of the difference between ‘affect’ and ‘effect’ and can more confidently use these terms. Remember, ‘affect’ is generally used as a verb and signifies influence or the act of changing something, while ‘effect’ is typically used as a noun, indicating a result or outcome.
Remember the acronyms RAVEN (Remember Affect Verb Effect Noun) and the hints ‘A for Action’ (affect) and ‘E for End result’ (effect) to help distinguish between the two. Though there are exceptions, these rules cover the majority of cases and provide a solid foundation for discerning when to use ‘affect’ or ‘effect.’
Affect vs. Effect Quiz
Before you go, put your knowledge to the test! Take our Affect vs. Effect Quiz and see if you can get a perfect score.


